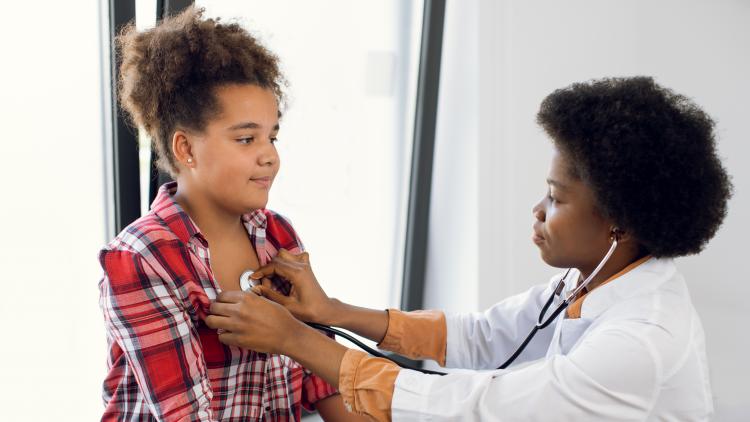
Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, the air passages that link the mouth and nose to the lungs. There are two types of bronchitis: acute and chronic. Acute bronchitis often results from a cold or other respiratory infection and clears up in 2-4 weeks. Chronic bronchitis is persistent, coming back repeatedly and often not even clearing up completely. Chronic bronchitis is also often associated with other respiratory problems, such as COPD.
While acute bronchitis is generally not seen as a big deal, chronic bronchitis can make your lungs a breeding ground for further infections. Chronic bronchitis requires medical treatment to manage and prevent it from creating bigger respiratory issues. Both forms of bronchitis can also advance to pneumonia if left untreated. This is typically characterized by a worsening of symptoms and requires immediate medical attention.
There are many causes for bronchitis. Acute bronchitis may be caused by:
There's not much you can do to avoid viral or bacterial infections other than the usual handwashing and boosting your immune system. You can avoid the environmental triggers, however, by wearing appropriate respiratory protection when you know you'll be exposed to those lung-irritating substances. This can help reduce your chances of getting acute bronchitis. Chronic bronchitis is caused by:
One of the genetic factors for chronic bronchitis is a condition called Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency. This is also called: AATD, Alpha-1, orInherited emphysema. This is an inherited condition that makes you more susceptible to lung and liver disease.
The main symptoms for both acute and chronic bronchitis are the same and include:
Additional chronic bronchitis symptoms include:
In both acute and chronic bronchitis, you should contact your doctor if you notice:
When treating bronchitis, the first thing to realize is that antibiotics will not treat it if it's caused by a virus or exposure to lung-irritating elements. Even if bronchitis is caused by a bacterial infection, antibiotics are still not recommended and can actually do more harm than good. Taking antibiotics for bronchitis can lead to side effects such as a minor rash or more significant ones like antibiotic-resistant infections and C.diff infection. The best treatments for both acute and chronic bronchitis are:

Did you know that detoxing has been around for centuries? It's a way to make your body function more effectively and efficiently. The two most popular...

Arthritis refers to joint inflammation or tenderness. Arthritis causes this joint stiffness. Arthritis can affect all joints in the body, including fi...
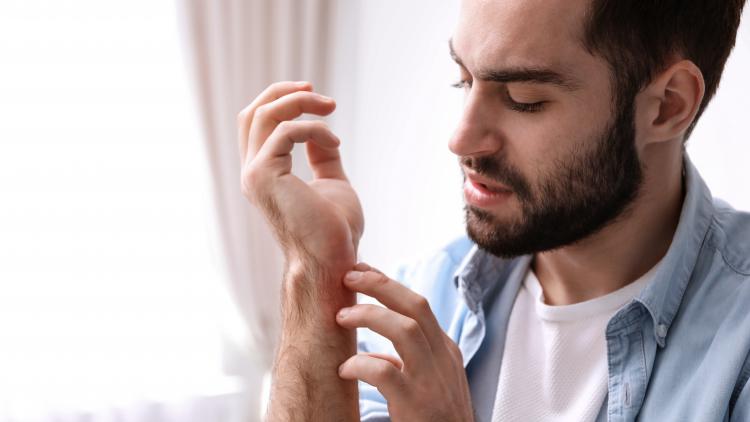
Eczema, also called atopic dermatitis, is a non-lethal medical condition associated with a profound negative impact on the quality of life. Characteri...